Dysplasia of the hip joint and congenital hip dislocation in in-fants
Dysplasia is a Greek word for development deformation, in our case that of the hip joint. Causative factors for such deformation of the hip joint can be mother's disease during the first half of pregnancy period, intoxication, injury etc. Unfavorable environmental conditions at mother's permanent place of residence or work may also represent significant influence factors.
In the postnatal period dysplasia of the hip joint can be diagnosed during an orthopedic checkup at the maternity hospital or an out-patients' clinic. There are three kinds of hip joint dysplasia:
- Dysplasia of the hip joint as a deformation of cotyloid cavity, femoral head and femoral neck, but with regular relation of articular surfaces,
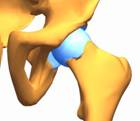
Congenital subluxation of the femoral head when, along with deformed cotyloid cavity, femoral head and femoral neck, relations of articular surfaces are irregular, the femoral head is displaced outwards, with possible location on the very edge of the joint,
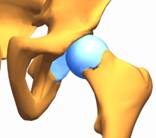
Congenital hip dislocation. The most severe form of hip joint dysplasia. In addition to a deforma-tion of the joint, articular surfaces completely loose mutual contact, the femoral head is dislocated out of the cotyloid cavity in lateral and upward direction.
Dysplasia of the hip joint and c ongenital hip dislocation can be diagnosed immediately after the infant is born on the following main symptoms:
1. Limited abduction in one or both hip joints of the baby. The symptom is detected as follows: infant's legs are bent at right angle in hip and knee joints and moved apart until they reach a stop. A normal angle of hip abduction is between 160 and 180 ° . In case of hip joint dysplasia this angle is limited.
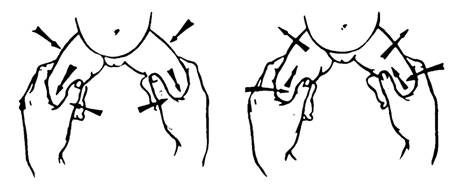
2. Marx-Ortolani or УclickФ symptom. This symptom is detectable only if the baby is aged under 3 months, at an older age it disappears. Detection procedure is as follows: infant's legs are bent at right angle in knee and hip joints, then placed along the body's vertical axis and slowly moved apart. During this procedure a click on the side of dislocation is audible, while the leg flinches. The click may be audible at some distance.
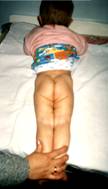
3. Visual shortness of the infant's leg. Detection procedure is as follows: baby's legs are bent in knee and hip joints and symmetrically pressed against the stomach. The level of the knee joint position will show whether the corresponding limb is shorter.

4. Skin fold asymmetry is detected at the front and the rear of the body with baby's legs straightened. Frontal inguinal folds in a healthy infant should be symmetrical. The same applies to rear gluteal and popliteal folds. Their asymmetry is a sign of the hip joint dysplasia. However, this symptom is inconsistent and of a minor significance.
Should you detect the above signs in your baby, you must urgently see a pediatric orthopedist, since a neglected hip joint dysplasia in infancy leads to development of dysontogenetic coxarthrosis at adult age. According to the Central Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics (CITO), dysontogenetic coxarthrosis develops already in people aged over 25 accounting for 75% of all hip joint diseases in adults. Treatment of this pathology in adults in most cases is only possible through implantation of an endoprosthesis, i.e. substitution of the affected joint for a metal implant. If not cured, a subluxation of the hip causes pain in the joint, and the child starts limping at the age of 3 to 5 years. A congenital hip dislocation results in limping or waddling gait immediately after the child begins to walk.
In Togliatti , I adopt since 1989 a new method of hip dysplasia therapy without fixation implements, which does not provoke abnormalities in physical development of children. The originality of this method is confirmed by the Russian patent УA method of congenital hip dislocation treatmentФ no. 2102945 dated 27.01.1998.

It is based on manipulations of infant's hip joints aimed at reduction of the hip head and its holding in the correct position by stretching hip adductor muscles. Therapy using this method is performed by me personally in the outpatient setting.
The above manipulations are to be carried out as a course on a daily basis 5 sessions per week. The number of therapy courses depends on child's age and severity of the disease. On average 1 to 3 courses are required. Pain from manipulations is moderate and ceases immediately after the session. As a result of treatment the range of hip joint motions increases up to normal, asymmetry in hip abduction disappears, the femoral head becomes easily palpable.
Such kind of therapy usually makes infants mobile and promotes their ability to stand up and seat. Their physical development also accelerates. Neurological symptoms, if any, abate. Immediately after treatment the baby can be put on his feet and taught walking.
During subsequent months, before the baby begins to walk, remedial physical exercises for hip joints and massage of gluteal and hip muscles are performed. 6 months after the therapy, an X-ray print to check hip joint is taken. Positive results of treatment are stated with 99.5 percent of children. No physical development lag was noted. An overwhelming majority of children began to walk towards the age of 1 year.
Treatment of congenital dislocations in infants with the femoral head slipped out of the position reached after reduction, is performed in a different way.
After a course of treatment for femoral head reduction using the above method, infant's legs are fixed by a plaster bandage of Vinogradov in Lorenz position 1 for a period of 3 to 4 months.

A clinical example is shown on X-ray prints of Yulia, aged 4 months.
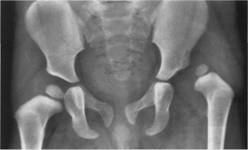 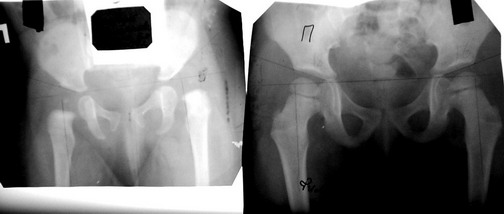
Before and after the treatment
My recommendations for parents on remedial physical exercises with hip joint dysplasia:
Put the baby on the table in dorsal position, with his legs towards you.
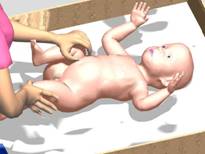
Do a short massage of gluteal and hip muscles for 2 to 3 minutes.
Bend the baby's legs in knee and hip joints at the right angle and press them to the stomach.
Carry out rotational motions with hips in opposite directions without applying force, abducting hips gradually for 10 minutes.
 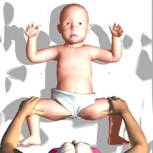
The last exercise is called УpedalingФ. It consists in bending and unbending alternately baby's legs.
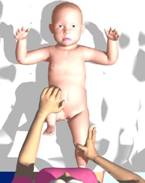
It is recommended to do therapeutic exercises twice a day until the baby has learned to walk well. During the same period it is recommended to do massage: 10 sessions 3-4 courses a year.
In the course of therapeutic exercises the baby may become capricious, jib, do not let do exercises. In such cases wait a bit until he relaxes his legs, then resume exercises. The most essential thing you must remember when performing remedial exercises is not to apply force. So you will never inflict an injury to the baby. During the treatment you may put the baby on his feet to form a reflex of support and walking.
At the end I would like to stress once more for parents that congenital hip joint dysplasia and congenital hip dislocation can be cured quickly and effectively only under condition that the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, at the infant's age of 3 to 12 months. If you follow my recommendations, you will bring up a healthy and nice child.
Up
|


